Research contents
Fukubayashi Lab
◆RESEARCH FIELD
Geotechnical Engineering, Road Engineering,International Cooperation,Intermediate
land infrastructure development,SDGs
Road infrastructure development using Do-nou course material
Although
urban roads and hightway are being developed in developing countries, roads in
rural areas are often in a natural ground or unpaved. In the rainy season, the
road surface becomes muddy and trafficability is not secured , making it
difficult to access hospitals, schools and markets. Therefore, we have
developed and applied a method using Do-nou for the purpose of improving the
accessibility of farm roads by using local materials and human resources. We
are conducting research toward establishing roadbed design guidelines using Do-nou
construction for further diffusion and retention

Deformation characteristics of base course consisting of Do-nou
In this study, it is aimed to establish the design guideline by modifying
the existing unpaved road design guideline in Ethiopia, where specifying
the thickness of base; based on type of material, bearing capacity of subgrade
and traffic load. The series of full-size driving tests have been conducted
to refer the performance of base course designed with the existing guideline
and of that consisting of do-nou as to deformation at a certain number
of run of the truck.
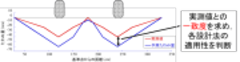
Application of multi-layered elastic theory to design road base using Do-nou for unpaved road
In rural area of developing countries, Do-nou is often applied to road base to improve trafficability of unpaved road. The design for the structure of road base consisting of Do-nou, such as number of layers, has been decided based on the judgment of the experienced engineer. In order to disseminate the method to build road base with Do-nou, a standard design guideline need to be developed. On this regard, in this study, it was examined if multi-layered elastic theory for pavement design could be applied to decide the thickness of road base consisting of crushed stones with Do-nou and without Do-nou for unpaved road. The applicability has been compared with those of gravel road design of the AASHTO and low volume road design guideline in Ethiopia. Compared the deformation of road surface predicted with the design methods with that measured during the actual full-size driving tests, it was found that the elastic modulus of base layer with and without Do-nou were smaller than those utilized for paved road design.
Study on degree of compaction of backfill of Do-nou
Do-nou application dose not require compaction equipment. Though the number of application of Do-nou to road base course increases, the standard construction management method has not been established. In this paper, it is aimed to develop management method of degree of compaction of backfill of Do-nou. The compaction is conducted by blows of hand rammer with a certain weight.Impact assessment of public participation projects in developing country
Road infrastructure development of rural area and agricultural area in developing country has been delayed. Since residents are crossing the riverbed , the road will be cut off if the water level rises due to rainfall. In order to contribute to sustainable development (SDGs) where no one is left behind , a case study will be conducted to examine the approach and its applicability to support infrastructure development through public participation and local resources. A overflow bridge was constructed in crossing area of a farm road in the Philippines in collaboration with the government, NGOs , and residents. A field survey is being conducted to understand the usefulness of the overflow bridge structure and the impact on the surrounding area.

Impact assessment and application of overflow bridge construction project through community participation in the Philippines
Two overflow bridge were constructed in collaboration with local government,
community and NGO in the rural area of the Philippines in 2015 and 2017
to improve the passage quality at the crossings. Both bridges were constructed
using Do-nou, though only one bridge had grider structuer. Both projects
were constructed through the local government, residents and NGO. It was assumed that the structure of the overflow bridge was reasonable considering feasibility and limited budget and that the project through community collaboration generate ownership among the local government and community thus the overflow bridge are maintained sustainably.
Prediction sediment disasters on Route 220
Route
220, which connects Miyazaki and Kagoshima prefectures , is frequently subjected
to prior traffic regulation, and slope failures frequently occur due to
sediment disasters, which have a significant impact on commuting, school
attending and socio-economic activities. An annual disaster prevention medical
record inspection is conducted to minimize damage. As a result, slopes that
have been diagnosed as "necessary measures" have a high risk of
collapsing, but countermeasures cannot be carried out at once in all places.
Therefore, if the risks can be ranked, efficient measures can be taken. In this
research, we are conducting a research for predicting the occurrence of
sediment disasters on Route 220 by statistical methods based on the data of
disaster prevention medical records.
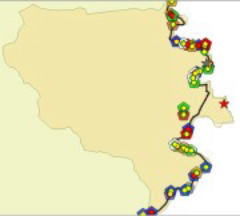
Applicability of statistical methods to estimate probablity of sediment disasters on National Route 220
In this
paper, aiming to prioritize the slopes at Route 220 to be treated with slope
protection measure, stoical method to estimate probability of sediment
disasters has been applied using the comprehensive information and data
gathered through the annual inspection. Firstly, the existing data related to
the slope condition, land use, facilities along the route, hazard map, etc.
have been collected from several re-sources, and then summarized into GIS.